Figure 7.9 A sketch of the evolution of plant forms through geological periods NEET

Evolution of Form Meer
Our theory relates the separate evolutionary histories of plants and animals through the fundamental physics underlying their distinct overall forms and physiologies. allometric scaling|biological scaling|tree geometry|fractal U nderstanding the origin and evolution of the geometries of living forms is a formidable challenge (1, 2).

Evolution of Form Hejduk_3 Grid, Form architecture, Evolution
Evolution of Form and Function by Richard William Nelson | Dec 29, 2016 00:00 00:00 To think that shape affects function - or form follows function - is an implicit assertion used ubiquitously throughout the evolution industry. This assumption, however, is untested.
ADVANCED COURSE FUNCTIONAL MORPHOLOGY EVOLUTION OF FORM AND FUNCTION FROM INDIVIDUALS TO
evolution, theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants, animals, and other living things on Earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations. The theory of evolution is one of the fundamental keystones of modern biological theory.. The diversity of the living world is staggering.
Figure 7.9 A sketch of the evolution of plant forms through geological periods NEET
Another piece of evidence of evolution is the convergence of form in organisms that share similar environments. For example, species of unrelated animals, such as the arctic fox and ptarmigan, living in the arctic region have been selected for seasonal white phenotypes during winter to blend with the snow and ice (Figure 18.8). These.
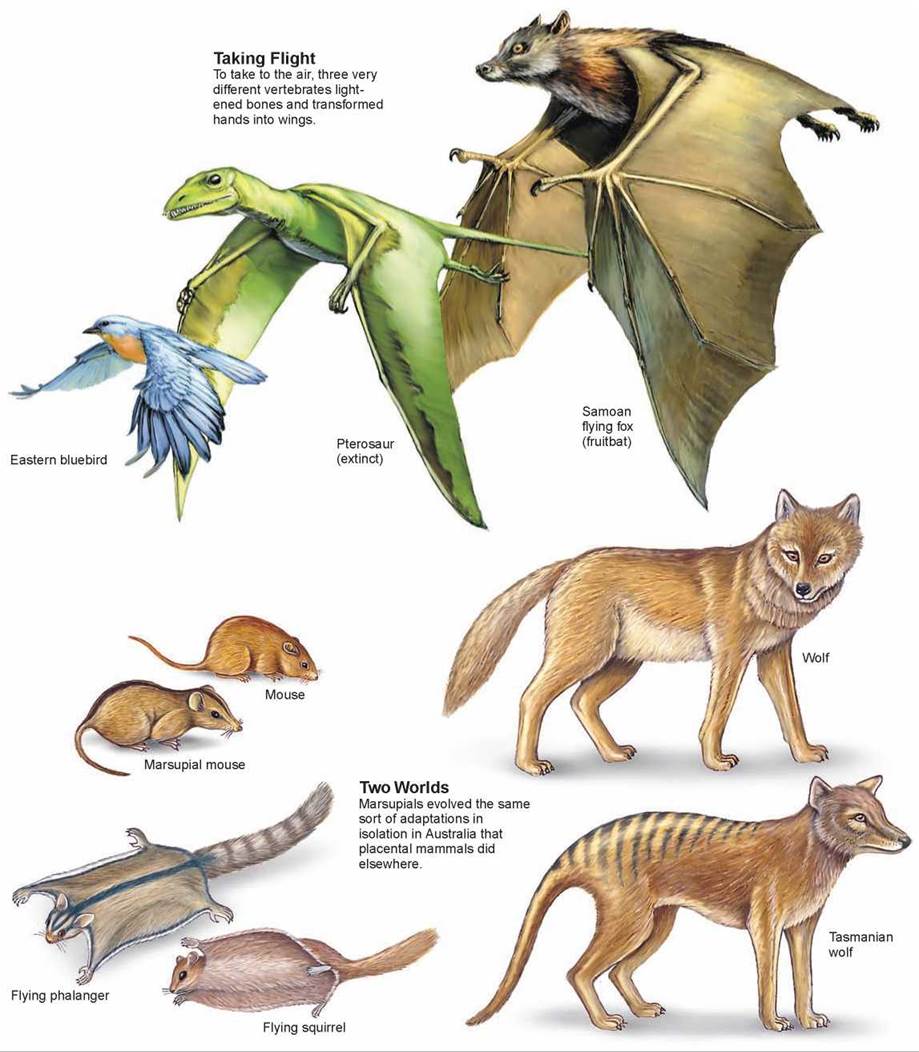
Figure 14.17. Convergent evolution many paths to one goal.
Figure 18.1E. 1 18.1 E. 1: Evolution of Humans and Horses: (a) In this display, fossil hominids are arranged from oldest (bottom) to newest (top). As hominids evolved, the shape of the skull changed. (b) An artist's rendition of extinct species of the genus Equus reveals that these ancient species resembled the modern horse (Equus ferus), but.

Raymond Loewy's Illustrative Chart Showing the Evolution of Form Factors Core77
Broadly speaking, evolution is a change in the genetic makeup (and often, the heritable features) of a population over time. Biologists sometimes define two types of evolution based on scale: Macroevolution, which refers to large-scale changes that occur over extended time periods, such as the formation of new species and groups.

AWM Evolution of Forms
In summary, we propose that the life process is based not on genetic variation, but on the second law of thermodynamics (hereinafter the second law) and the principle of least action, as proposed for thermodynamically open systems by De Maupertuis (Ville et al. 2008 ), which at the most fundamental level say the same thing.

“A Sequence From the Evolution of Form” by ISEA Symposium Archives
Darwin's seminal book, On the Origin of Species, set forth his ideas about evolution and natural selection.These ideas were largely based on direct observations from Darwin's travels around the globe. From 1831 to 1836, he was part of a survey expedition carried out by the ship HMS Beagle, which included stops in South America, Australia, and the southern tip of Africa.
Presidents Medals Courting Canopy
Significance Understanding the origin and evolution of the shapes observed in nature remains an exciting challenge. Even from a cursory inspection, it is clear that the shapes of animals and plants, as determined by the distribution of mass over volume, are distinct.

Innovative solution to the evolution of form proposed
Evidence for large-scale evolution ( macroevolution) comes from anatomy and embryology, molecular biology, biogeography, and fossils. Similar anatomy found in different species may be homologous (shared due to ancestry) or analogous (shared due to similar selective pressures). Molecular similarities provide evidence for the shared ancestry of life.

The Evolution of Forms Autodesk Community Gallery
Evolution 101 The history of life: looking at the patternsChange over time and shared ancestors Mechanisms: the processes of evolutionSelection, mutation, migration, and more Evolution within a population How new species arise Evolution above the species level The big issuesPacing, diversity, complexity, and trends Teach Evolution

Schematic illustration of form evolution. The process of synthesizing... Download Scientific
Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominid family,. During this time period various forms of australopiths existed, including Australopithecus anamensis, Au. afarensis,.

Sean B Carroll Quote “Evolution of form is very much a matter of teaching very old genes new
human evolution, the process by which human beings developed on Earth from now-extinct primates. Viewed zoologically, we humans are Homo sapiens, a culture -bearing upright-walking species that lives on the ground and very likely first evolved in Africa about 315,000 years ago.

The evolution of form 7 in chain 6, from left to right. The first... Download Scientific Diagram
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation,. Evolution influences every aspect of the form and behaviour of organisms. Most prominent are the specific.

William Latham The evolution of form (1990) MutatorVR
Life - Evolution, History, Earth: The evidence is overwhelming that all life on Earth has evolved from common ancestors in an unbroken chain since its origin. Darwin's principle of evolution is summarized by the following facts. All life tends to increase: more organisms are conceived, born, hatched, germinated from seed, sprouted from spores, or produced by cell division (or other means.

Form design by Chihlin Chiang at
The sequential steps involved in creating double-shell hollow MOF are shown in Fig. 2: (1) single-crystal to single-crystal transformation from MOP to MOF through postsynthetic linker insertion.