Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction, Free PDF Download Learn Bright

Wave Behavior Education site
Reflection is the phenomenon wherein a beam of light incident on an object bounces off, i.e., reflects of its surface. The actual amount of light that is reflected depends on the composition and physical characteristics of the object.

Refraction Definition, Examples, & Facts Britannica
The law of refraction, also known as Snell's law, describes the relationship between the angle of incidence (θ 1) and the angle of refraction (θ 2 ), measured with respect to the normal ("perpendicular line") to the surface, in mathematical terms: n1 sin θ 1 = n2 sin θ 2, where n1 and n2 are the index of refraction of the first and second media,.

Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction, Free PDF Download Learn Bright
Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction Interference of Waves The Doppler Effect Previously in Lesson 3, the behavior of waves traveling along a rope from a more dense medium to a less dense medium (and vice versa) was discussed. The wave doesn't just stop when it reaches the end of the medium.

Physics Reflection, Refraction, Diffraction YouTube
They can undergo refraction, reflection, interference and diffraction. These basic properties define the behaviour of a wave - anything that reflects, refracts, diffracts and interferes is labelled a wave. These behaviours of waves can help us understand how water waves interact with land. Out in the deep ocean, tsunamis and wind-generated.

Reflection, Refraction, And Diffraction Stock Vector Illustration 420573394 Shutterstock
Refraction. We saw that light waves have the capability of changing the direction of the rays associated with it through diffraction. We now consider another way that such a direction change can occur. This process, called refraction, comes about when a wave moves into a new medium. To get to the essence of this phenomenon from Huygens's.

Difference Reflectivity, Refraction and Diffraction of Light Reflective Solutions Information
Section Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Explain wave behavior of light, including diffraction and interference, including the role of constructive and destructive interference in Young's single-slit and double-slit experiments

Waves Properties Reflection Refraction Diffraction Physics Waves 3 YouTube
Diffraction patterns are typically studied behind an orifice cut in a screen. The effect is similar to diffraction by a small object, but it is then easier to observe, thanks to the absorption of non-diffracted light. Figure 2 thus represents the diffraction pattern of monochromatic light of wavelength λ passing through a slit of width a.

Reflection, Refraction and Diffraction The Science and Maths Zone
Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction Interference and Beats The Doppler Effect and Shock Waves Boundary Behavior Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction Like any wave, a sound wave doesn't just stop when it reaches the end of the medium or when it encounters an obstacle in its path.
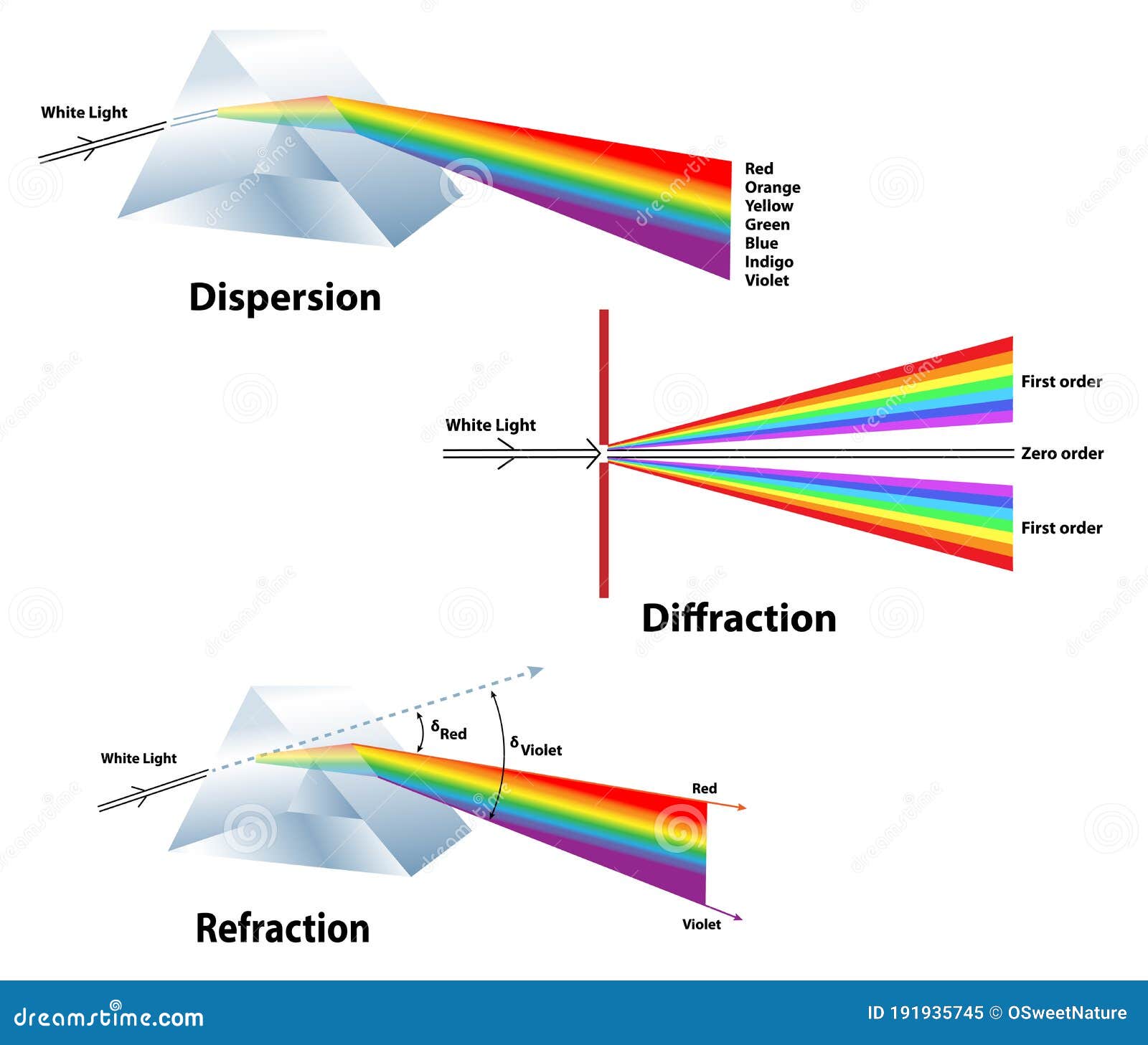
Diffraction refraction privatepoliz
Diffraction is the bending of light rays around an obstacle or through a gap. This results in the formation of an interference pattern. What are the three ways light travels? There are three ways.

Difference between Reflection,Refraction, and Diffraction YouTube
Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves around an obstacle. It is most pronounced when a light wave strikes an object with a size comparable to its own wavelength. An instrument called a spectrometer uses diffraction to separate light into a range of wavelengths—a spectrum.
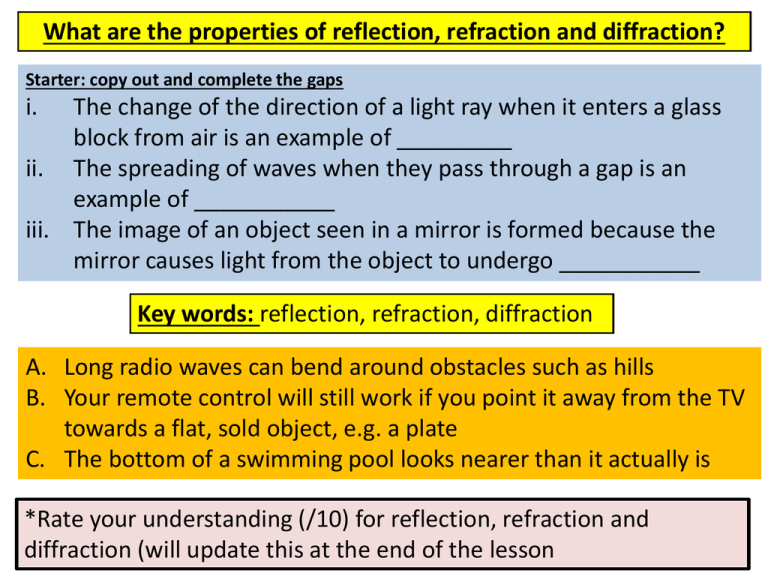
properties of reflection, refraction and diffraction
Reflection of light occurs when light rays strike a surface and bounce back or reflect off it. In this case, the Law of Reflection is valid, ie the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction is when light rays enter a different medium of different optical density and change direction or bend. In this case, Snell's Law is valid to calculate the degree of refraction. If it.

Reflection, Refraction and Diffraction The Science and Maths Zone
Diffraction is the concept that is explained using Huygens's Principle, and is defined as the bending of a wave around the edges of an opening or an obstacle. This principle can be used to define reflection, as shown in the figure. It can also be used to explain refraction and interference.
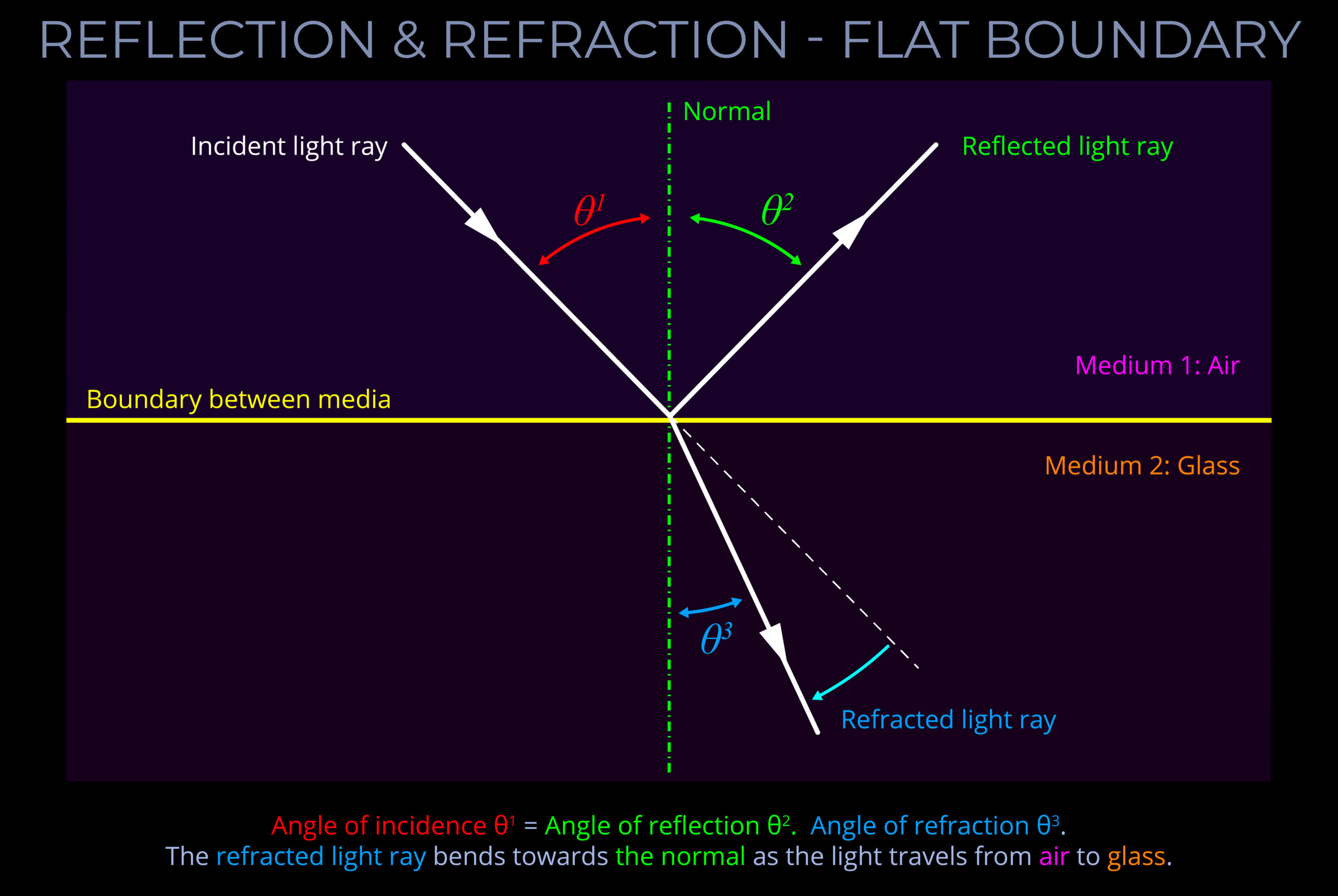
Reflection & Refraction Flat Boundary
The angles of reflection and refraction are given by Snell's law, but computing the fraction of the incident light that is reflected, transmitted, or dissipated within the periodic structure requires numerical analysis.. These hemispheres inform us of which diffraction orders are present in reflection and transmission. We initially center.

Reflection, Refraction, and Diffraction YouTube
There are two laws that govern how light changes direction when it interacts with matter: the law of reflection, for situations in which light bounces off matter; and the law of refraction, for situations in which light passes through matter. In this section, we consider the geometric optics of reflection.
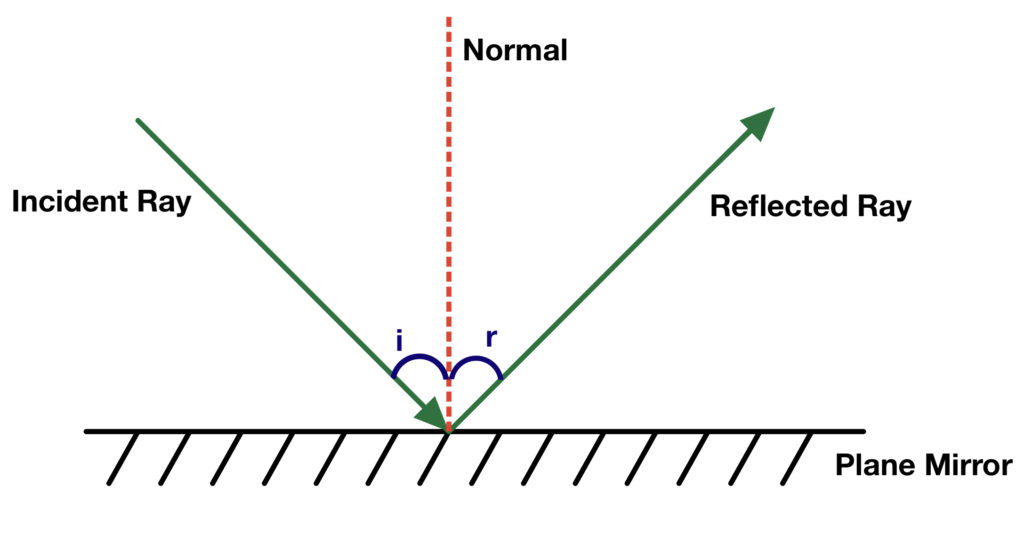
Reflection, Refraction and Diffraction The Science and Maths Zone
Difference between Reflection,Refraction, and Diffraction MooMooMath and Science 428K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 1.2K 113K views 2 years ago Waves such as light and sound waves can bend,.
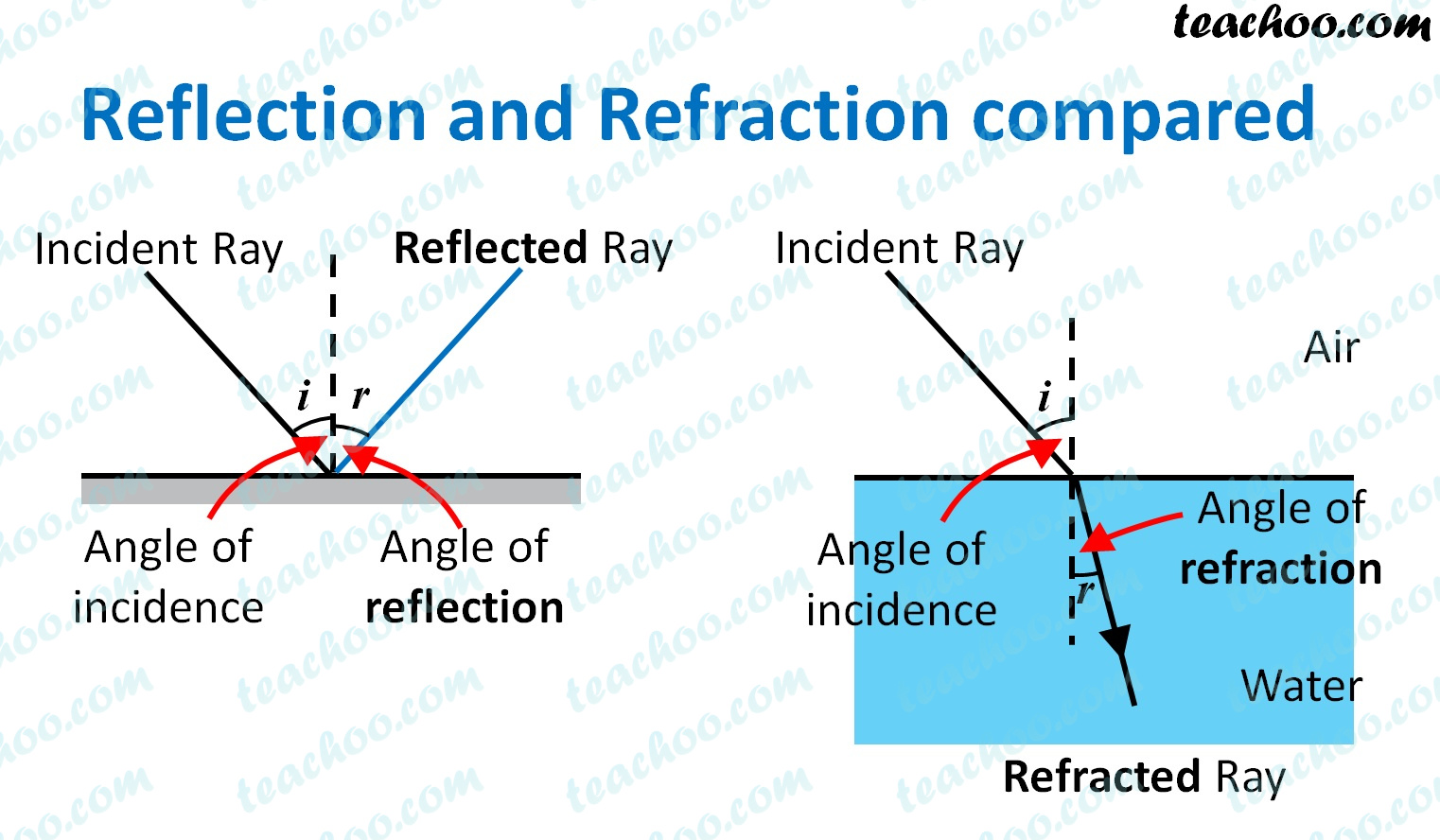
What is the difference between Reflection and Refraction? Teachoo
The angle of incidence (i) is the angle between the incident ray and normal; the angle of reflection (r) is the angle between the reflected ray and normal. Figure 1 Reflection of light off a mirror, with incident (I) and reflected (R) rays; and the angles of incidence (i) and reflection (r). i=r