
Costal Cartilage Injuries Radsource
Costovertebral Joints Introduction The costovertebral joints describe two groups of synovial plane joints which connect the proximal end of the ribs with their corresponding thoracic vertebrae, enclosing the thoracic cage from the posterior side. Joining of ribs to the vertebrae occurs at two places
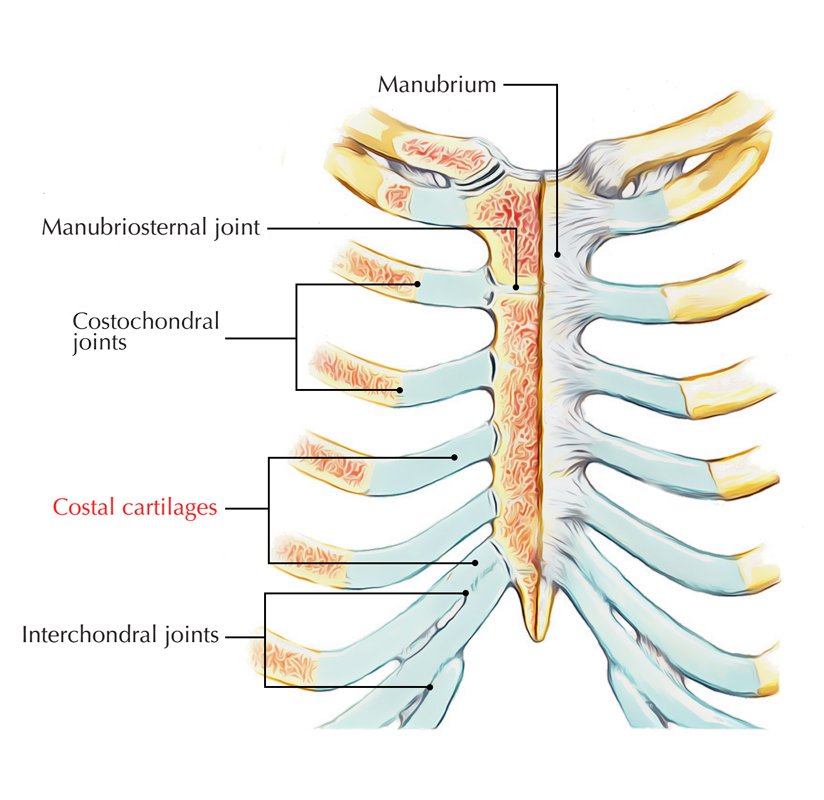
Costal Cartilages Earth's Lab
The costovertebral joints describe two groups of synovial plane joints which connect the proximal end of the ribs with their corresponding vertebrae, enclosing the thoracic cage from the posterior side. Precisely, these joints are described as;
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/body-of-rib/FnDyQ8NUSf99MdIRPOktQ_erSs1Zn9Up_Corpus_costae_02.png)
Body of rib (Corpus costae) Kenhub
Levatores costarum consists of 12 small triangular muscles that connect the thoracic vertebrae with the adjacent ribs.Located along either side of the posterior aspect of the thoracic vertebra they descend adjacent to the spine, spanning the thoracic region from C7 to T12 levels.. Together with the intercostal muscles, serratus posterior superior and inferior and transversus thoracis, they.

Anatomy Stock Images torsoribcageribscostaecostalcartilage
FMA. 7591. Anatomical terminology. [ edit on Wikidata] The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage [1] that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension.
Costal Anatomy Definition Anatomy Book
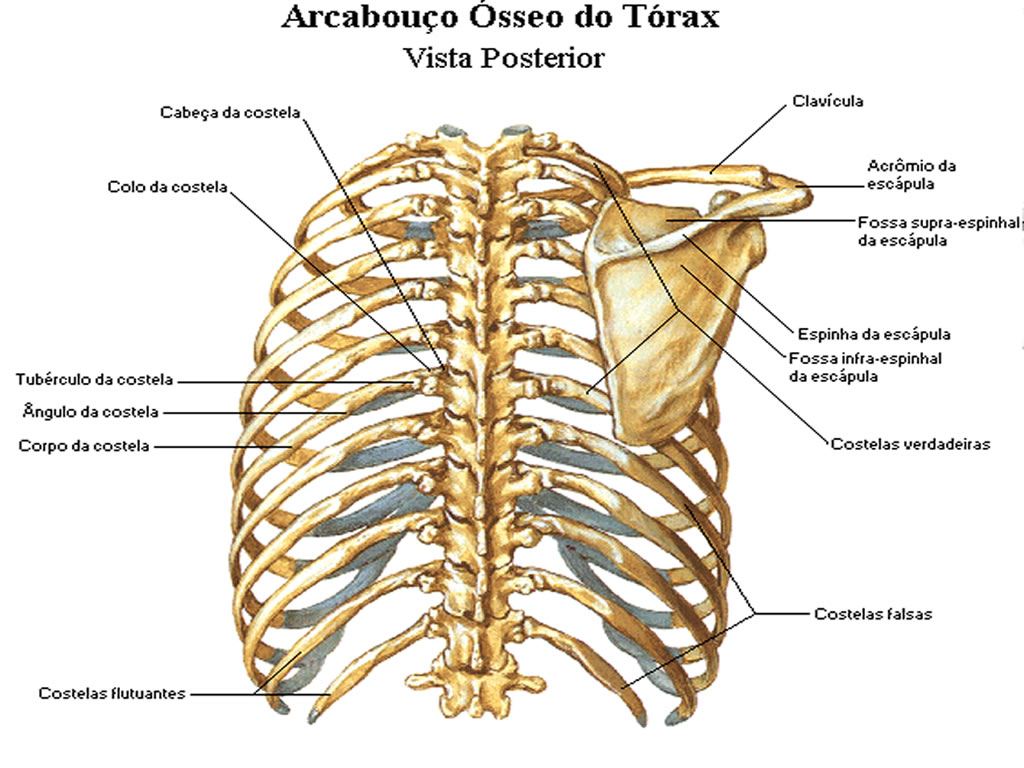
Structure of atypical ribs. First - widest, shortest, it has the sharpest curve and only one articular surface, contains two grooves for the subclavian vessels. Second - it has two facets and a roughened tuberosity on its posterior surface. Tenth, eleventh, twelfth - they have only one facet and neither a neck or tubercles.
Fisiologi Costa Pada Tubuh Manusia SIPATILMUKU
The thoracic wall consists of a bony framework held together by twelve thoracic vertebrae posteriorly, giving rise to ribs that encircle the lateral and anterior thoracic cavity. The first nine ribs curve around the lateral thoracic wall and connect to the manubrium and sternum. Ribs 10 to 12 are relatively short and attach to the costal margins of the ribs just above them. Ribs 10 to 12, due.
Shiatsu Anatomia
The costal cartilages are bars of hyaline cartilage which serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute very materially to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. The first seven pairs are connected with the sternum; the next three are each articulated with the lower border of the cartilage of the preceding rib; the last two have pointed extremities, which end in the wall of the abdomen.

Image result for costae
The combination of an acrocarpous condition (inferred based on a series of morphological features), a central conducting strand, a homogeneous leaf costa and a lamina with bistratose portions and sinuous cells, and multicellular gemmae, supports placement of Tricarinella in family Grimmiaceae.
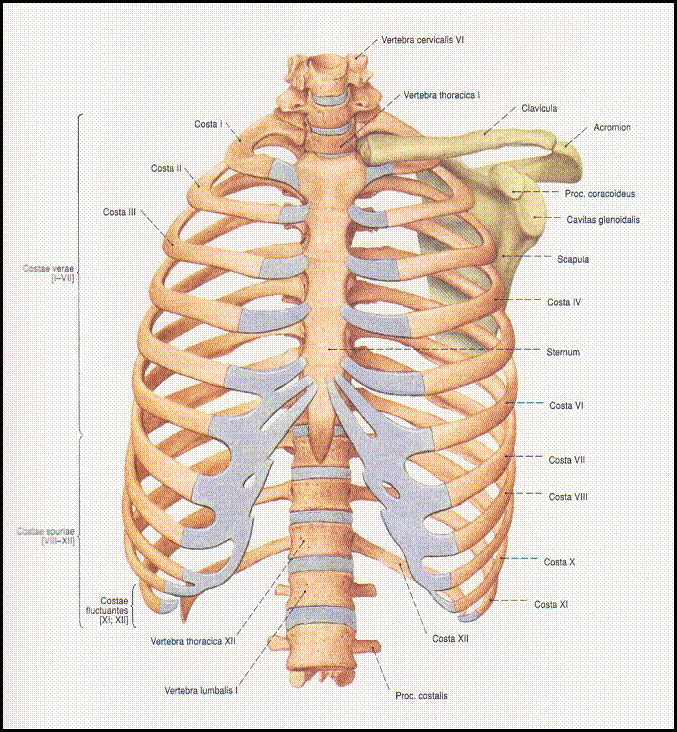
Buku Anatomi Bagian I
Sporophytes are matrotrophic, permanently attached to and at least partially dependent on the female gametophyte for nutrition, and are unbranched, determinate in growth, and monosporangiate. The gametophytes of mosses are small, usually perennial plants, comprising branched or unbranched shoot systems bearing spirally arranged leaves.

Schematic of the right thorax with the lateral costal artery depicted
The world's largest software site. The Best downloads for any device. New apps.

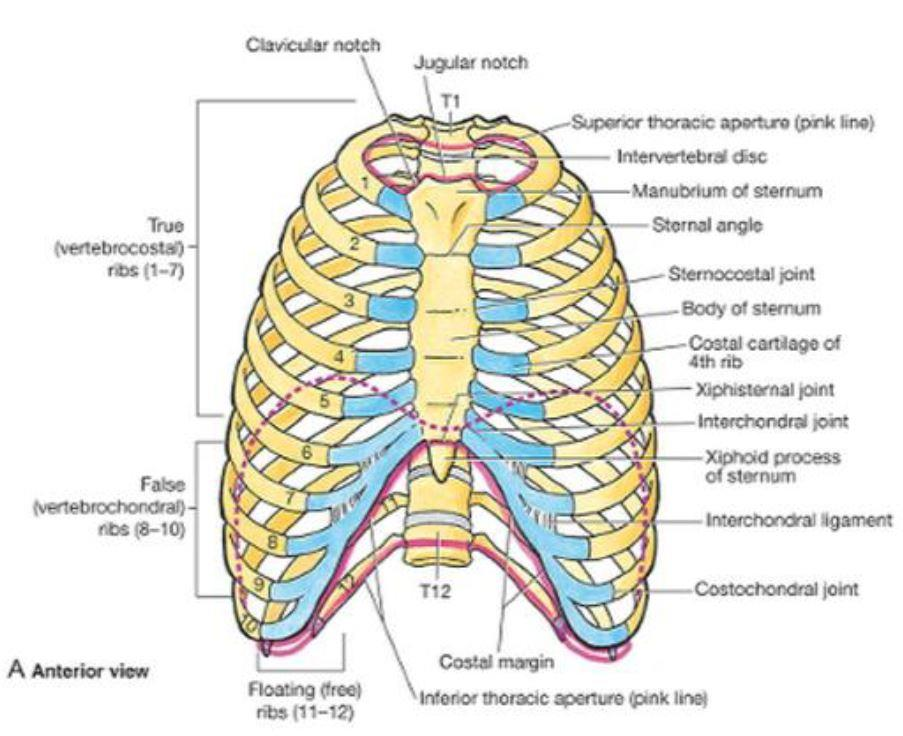
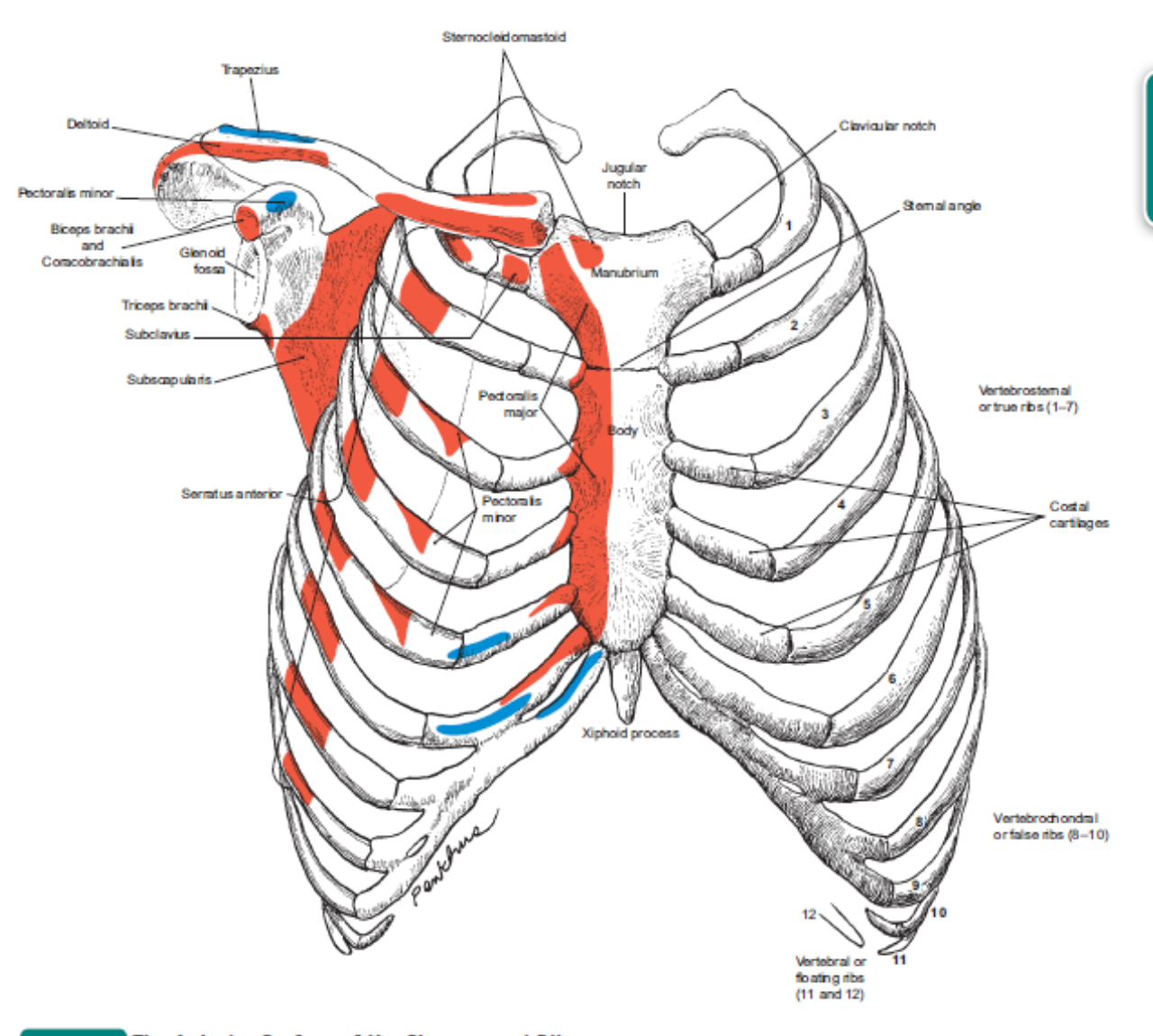
Ribs, Classification of Ribs & Costal Topography
The Classification of Human Ribs. The upper seven ribs are so-called "true ribs" as they have their cartilages directly attached to the sternum. Other (from 8 th to 12 th) are called "false ribs" as they attach to the sternum via other ribs cartilage.
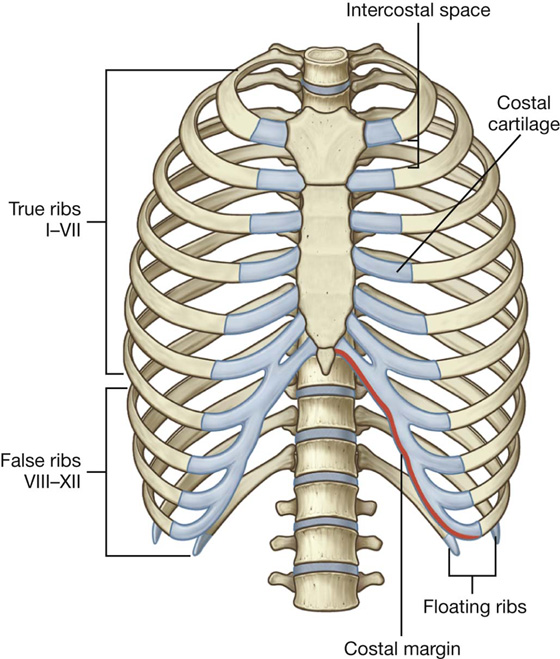
Costal Anatomy Definition Anatomy Book
The costal margin is a cartilaginous arch formed by the medial margins of the cartilages of ribs 7-10. The costal margin forms an arch that begins posteroinferiorly at the 10th costal cartilage and extends in an anterosuperior direction, terminating at the costal cartilage of rib 7, where it attaches to the body of sternum.

First rib (Costa I); Image Yousun Koh Anatomía, Atlas
We also found correlations between costa anatomy, peristome morphology, and the limbidium, which could reflect the evolutionary recruitment of genetic networks from the gametophyte to the sporophyte phase. The correlation found between average habitat moisture and the sexual system indicates that dioicous and polyoicous species are more likely.
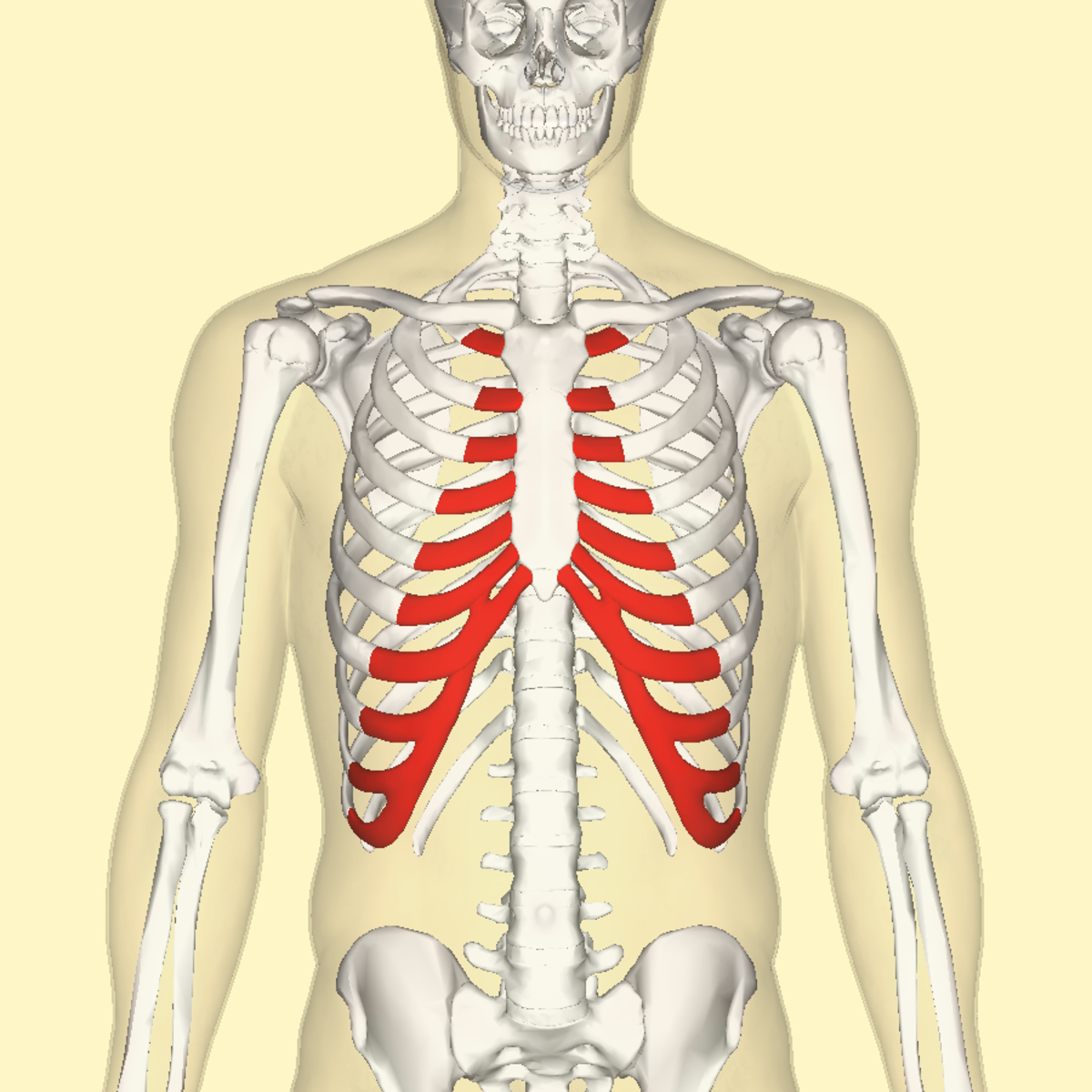
Costochondritis Feels Like a Heart Attack But It's Not HealDove
The costal or ventral surface presents a broad concavity, the subscapular fossa. The medial two-thirds of the fossa are marked by several oblique ridges, which run lateralward and upward. The ridges give attachment to the tendinous insertions, and the surfaces between them to the fleshy fibers, of the Subscapularis. The lateral third of the fossa is smooth and covered by the fibers of this muscle.

Anatomia dos Músculos das Costas em 3D YouTube
Morphology of some species of mosses found in ASPA 125 (Fildes Peninsula, King George Island). a-c Bartramia patens.a Leaf; b detail of papillae in the subula; c cross section of the leaf showing costa anatomy.d-e Polytrichastrum alpinum. d Cross section of leaf showing the lamellae; e detail of lamellae apical cells with thick walls.f-h Ditrichum hyalinum.
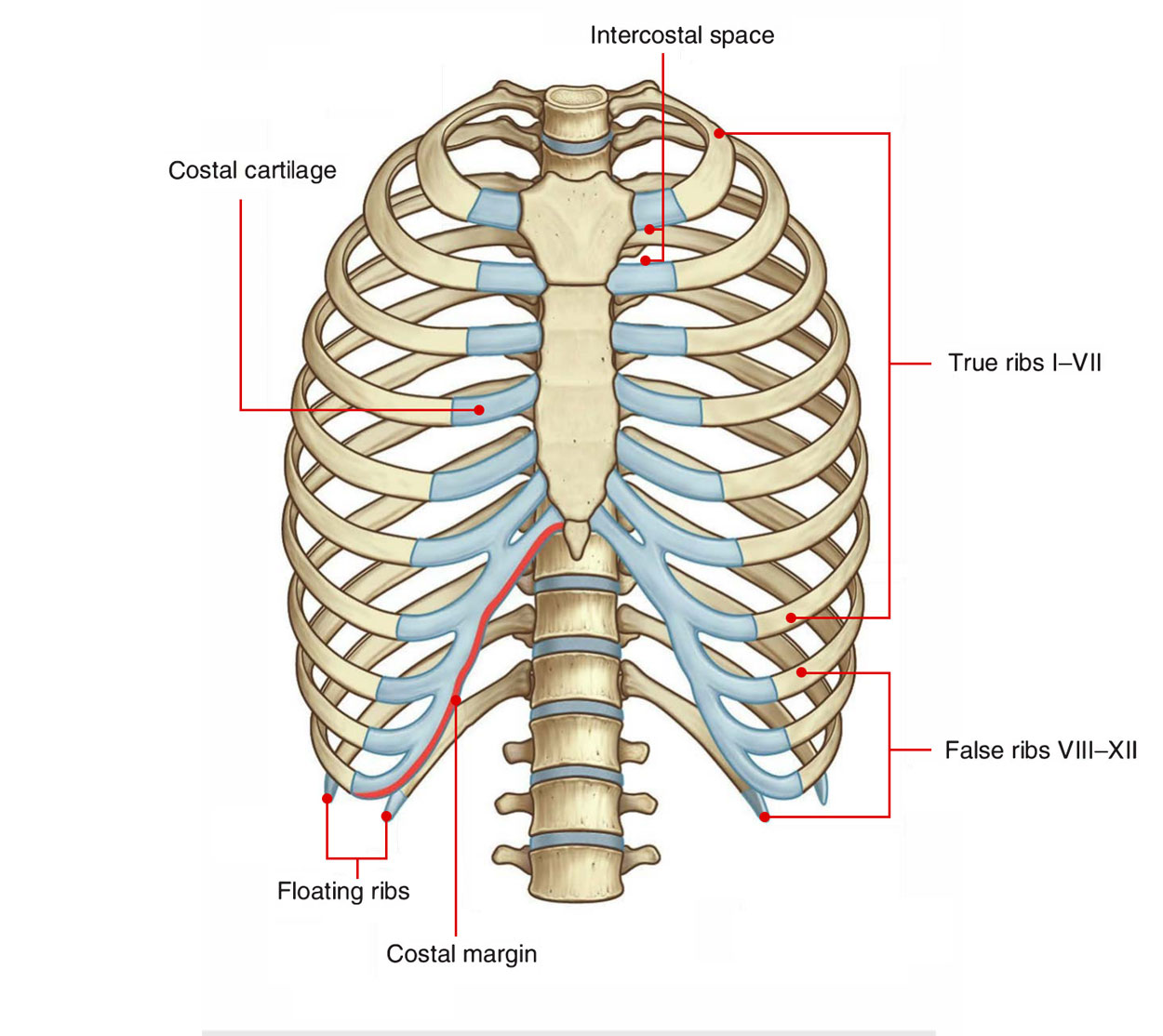
Costal Anatomy Definition Anatomy Book
Cervical ribs are supernumerary or accessory ribs arising from the seventh cervical vertebra.They occur in ~0.5% of the population, are usually bilateral, but often asymmetric 2, and are more common in females.. Related pathology. Although cervical ribs are usually asymptomatic, they are the most important anatomic rib variant clinically, because they can cause thoracic outlet syndrome by.